定义
JavaScript(缩写:JS)是一门完备的动态编程语言。当应用于 HTML 文档时,可为网站提供动态交互特性。由布兰登·艾克(Brendan Eich,Mozilla 项目、Mozilla 基金会和 Mozilla 公司的联合创始人)发明。
1. 什么是js
JavaScript 的应用场合极其广泛,简单到幻灯片、照片库、浮动布局和响应按钮点击,复杂到游戏、2D/3D 动画、大型数据库驱动程序等等。
JavaScript 相当简洁,却非常灵活。开发者们基于 JavaScript 核心编写了大量实用工具,可以使 开发工作事半功倍。其中包括:
- 浏览器应用程序接口(API)—— 浏览器内置的 API 提供了丰富的功能,比如:动态创建 HTML 和设置 CSS 样式、从用户的摄像头采集处理视频流、生成 3D 图像与音频样本等等。
- 第三方 API —— 让开发者可以在自己的站点中整合其它内容提供者(Twitter、Facebook 等)提供的功能。
- 第三方框架和库 —— 用来快速构建网站和应用。
2. 快速入门
2.1 变量
变量 (en-US) 是存储值的容器。要声明一个变量,先输入关键字 let 或 var,然后输入合适的名称:
let myVariable = 'Hello World'2.2 数据类型
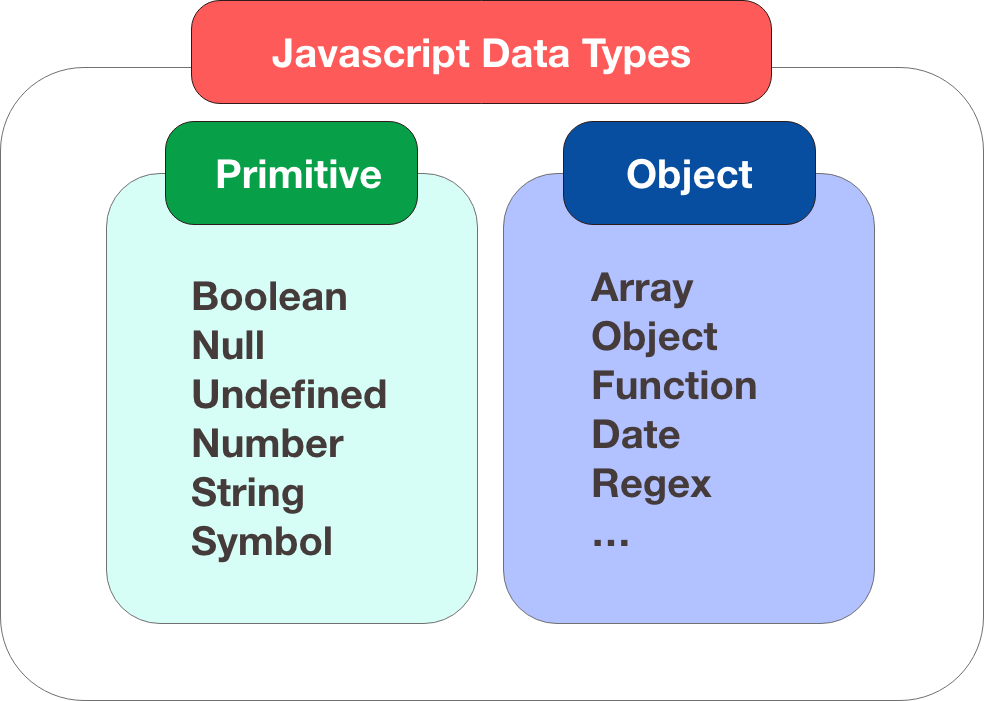
注意变量可以有不同的数据类型 :
- 值类型(基本类型):字符串(
String)、数字(Number)、布尔(Boolean)、空(Null)、未定义(Undefined)、Symbol。 - 引用数据类型(对象类型):对象(
Object)、数组(Array)、函数(Function),还有两个特殊的对象:正则(RegExp)和日期(Date)。
| 变量 | 解释 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| String | 字符串(一串文本):字符串的值必须用引号(单双均可,必须成对)扩起来。 | let myVariable = '李雷'; |
| Number | 数字:无需引号。 | let myVariable = 10; |
| Boolean | 布尔值(真 / 假): true/false 是 JS 里的特殊关键字,无需引号。 | let myVariable = true; |
| Array | 数组:用于在单一引用中存储多个值的结构。 | let myVariable = [1, '李雷', '韩梅梅', 10]; |
| Object | 对象:JavaScript 里一切皆对象,一切皆可储存在变量里。这一点要牢记于心。 | let myVariable = document.querySelector('h1'); |
2.3 运算符
运算符 (en-US) 是一类数学符号,可以根据两个值(或变量)产生结果。以下表格中介绍了一些最简单的运算符,可以在浏览器控制台里尝试一下后面的示例。
| 运算符 | 解释 | 符号 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 加 | 将两个数字相加,或拼接两个字符串。 | + | 6 + 9; "Hello " + "world!"; |
| 减、乘、除 | 这些运算符操作与基础算术一致。只是乘法写作星号,除法写作斜杠。 | -, *, / | 9 - 3; 8 * 2; 9 / 3; |
| 赋值运算符 | 为变量赋值(你之前已经见过这个符号了) | = | let myVariable = '李雷'; |
| 等于 | 测试两个值是否相等,并返回一个 true/false (布尔)值。 | === | let myVariable = 3; myVariable === 4; // false |
| 不等于 | 和等于运算符相反,测试两个值是否不相等,并返回一个 true/false (布尔)值。 | !== | let myVariable = 3; myVariable !== 3; // false |
| 取非 | 返回逻辑相反的值,比如当前值为真,则返回 false。 | ! | let myVariable = 3; !(myVariable === 3); // false |
2.4 条件语句
条件语句是一种代码结构,用来测试表达式的真假,并根据测试结果运行不同的代码。一个常用的条件语句是 if ... else。
// if...else
let num = 10;
if (num > 0) {
alert('正数');
} else {
alert('负数');
}
// switch...case
const day = new Date().getDate()
switch (day) {
case 0, 6:
alert('周末');
default:
alert('工作日');
}2.5 函数
函数用来封装可复用的功能。如果没有函数,一段特定的操作过程用几次就要重复写几次,而使用函数则只需写下函数名和一些简短的信息。
document.querySelector 和 alert 是浏览器内置的函数。下面代码演示的是如何自定义函数:
function multiply(num1, num2) {
return num1 * num2;
}2.6 事件
事件能为网页添加真实的交互能力。它可以捕捉浏览器操作并运行一些代码做为响应。最简单的事件是点击事件,鼠标的点击操作会触发该事件。
<button id="btn1">click</button>
<script>
const btn1 = document.getElementById('btn1')
// 只会触发最后定义的
btn1.onclick = () => {
console.log('clicked me')
}
// 添加多少个,会触发多少次
btn1.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('clicked me')
})
</script>3. 事件循环
3.1 定义
Event Loop即事件循环,是指浏览器或Node的一种解决javaScript单线程运行时不会阻塞的一种机制,也就是我们经常使用异步的原理。
3.2 微任务和宏任务
在JavaScript中,任务被分为两种,一种宏任务(MacroTask)也叫Task,一种叫微任务(MicroTask)。
- MacroTask(宏任务)setTimeout、setInterval、I/O、UI Rendering。
- MicroTask(微任务) Process.nextTick(Node独有)、Promise、Object.observe(废弃)、MutationObserver
3.3 执行过程
- 同步代码,调用栈执行后直接出栈
- 异步代码,放到Web API中,等待时机,等合适的时候放入回调队列(callbackQueue),等到调用栈空时eventLoop开始工作,轮询
- 微任务执行时机比宏任务要早
3.4 整体流程
- 先清空call stack中的同步代码
- 执行微任务队列中的微任务
- 尝试DOM渲染
- 触发Event Loop反复询问callbackQueue中是否有要执行的语句,有则放入call back继续执行
4. 原型
4.1 构造函数
构造函数模式的目的就是为了创建一个自定义类,并且创建这个类的实例。构造函数模式中拥有了类和实例的概念,并且实例和实例之间是相互独立的。
构造函数就是一个普通的函数,创建方式和普通函数没有区别,不同的是构造函数习惯上首字母大写。另外就是调用方式的不同,普通函数是直接调用,而构造函数需要使用new关键字来调用。
function Person(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
this.gender = gender
this.getInfo = function () {
return `${name} is a ${age} years old ${gender}`
}
}
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name
}
const p1 = new Person('lzugis', 18, 'boy')
console.log(p1.getInfo())4.2 原型
在JavaScript中,每当定义一个函数数据类型(普通函数、类)时候,都会天生自带一个prototype属性,这个属性指向函数的原型对象,并且这个属性是一个对象数据类型的值。 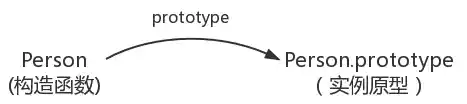
4.3 __proto__和constructor
每一个对象数据类型(普通的对象、实例、prototype......)也天生自带一个属性__proto__,属性值是当前实例所属类的原型(prototype)。原型对象中有一个属性constructor, 它指向函数对象。
function Person() {}
var person = new Person()
console.log(person.__proto__ === Person.prototype)//true
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor===Person)//true
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(person) === Person.prototype) // true4.4 原型链
在JavaScript中万物都是对象,对象和对象之间也有关系,并不是孤立存在的。对象之间的继承关系,在JavaScript中是通过prototype对象指向父类对象,直到指向Object对象为止,这样就形成了一个原型指向的链条,专业术语称之为原型链。
举例说明:person → Person → Object ,普通人继承人类,人类继承对象类
当我们访问对象的一个属性或方法时,它会先在对象自身中寻找,如果有则直接使用,如果没有则会去原型对象中寻找,如果找到则直接使用。如果没有则去原型的原型中寻找,直到找到Object对象的原型,Object对象的原型没有原型,如果在Object原型中依然没有找到,则返回undefined。
我们可以使用对象的hasOwnProperty()来检查对象自身中是否含有该属性;使用in检查对象中是否含有某个属性时,如果对象中没有但是原型中有,也会返回true 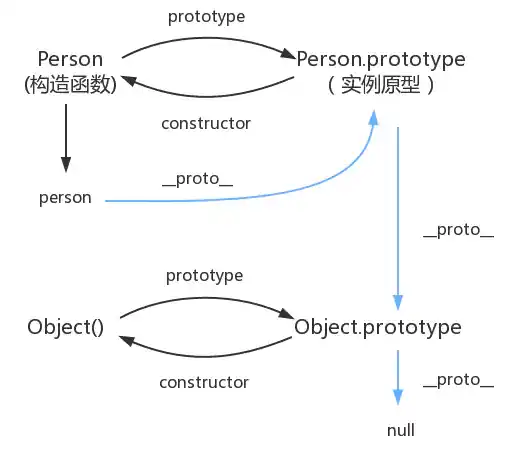
5. es6
5.1 概念
ECMAScript 6.0(以下简称 ES6)是 JavaScript 语言的下一代标准,已经在 2015 年 6 月正式发布了。它的目标,是使得 JavaScript 语言可以用来编写复杂的大型应用程序,成为企业级开发语言。
5.2 变量声明:const和let
// let - 块级作用域,可重新赋值
let count = 0;
count = 1;
// const - 块级作用域,不可重新赋值
const PI = 3.14159;
// PI = 3.14; // Error: Assignment to constant variable
// 块级作用域示例
function testScope() {
if (true) {
let blockLet = 'block scope';
const blockConst = 'block scope';
var blockVar = 'function scope';
}
// console.log(blockLet); // ReferenceError
// console.log(blockConst); // ReferenceError
console.log(blockVar); // 'function scope'
}5.3 模板字符串
const name = 'John';
const age = 30;
// 基本用法
const message = `My name is ${name} and I'm ${age} years old.`;
// 多行字符串
const template = `
<div class="user">
<h2>${name}</h2>
<p>Age: ${age}</p>
</div>
`;
// 表达式计算
const price = 100;
const tax = 0.08;
const total = `Total: $${(price * (1 + tax)).toFixed(2)}`;5.4 箭头函数
// 传统函数
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// 箭头函数
const addArrow = (a, b) => a + b;
// 多行箭头函数
const multiply = (a, b) => {
const result = a * b;
return result;
};
// this 绑定差异
const person = {
name: 'John',
// 传统函数:this指向调用者
sayHello: function() {
console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}`);
},
// 箭头函数:this指向定义时上下文
sayHelloArrow: () => {
console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}`); // undefined
}
};5.5 函数参数默认值
// 默认参数
function greet(name = 'Guest', message = 'Welcome') {
return `${message}, ${name}!`;
}
// 解构赋值默认值
function createUser({ name = 'Anonymous', age = 0, city = 'Unknown' } = {}) {
return { name, age, city };
}
// 使用示例
console.log(greet()); // "Welcome, Guest!"
console.log(greet('John', 'Hello')); // "Hello, John!"
console.log(createUser({ name: 'Alice', age: 25 })); // { name: 'Alice', age: 25, city: 'Unknown' }5.6 Spread / Rest 操作符
// Spread - 展开数组/对象
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
const arr2 = [...arr1, 4, 5]; // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
const obj1 = { name: 'John', age: 30 };
const obj2 = { ...obj1, city: 'New York' }; // { name: 'John', age: 30, city: 'New York' }
// Rest - 收集参数
function sum(...numbers) {
return numbers.reduce((total, num) => total + num, 0);
}
// 数组解构中的Rest
const [first, ...rest] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // first=1, rest=[2,3,4,5]5.7 对象和数组解构
// 数组解构
const colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue'];
const [primary, secondary, tertiary] = colors;
// 跳过元素
const [, , third] = colors; // third = 'blue'
// 对象解构
const user = {
name: 'John',
age: 30,
address: {
city: 'New York',
country: 'USA'
}
};
const { name, age } = user;
const { name: userName, age: userAge } = user; // 重命名
// 嵌套解构
const { address: { city, country } } = user;
// 函数参数解构
function displayUser({ name, age = 0, city = 'Unknown' }) {
console.log(`${name}, ${age}, lives in ${city}`);
}5.8 for...of 和 for...in
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
// for...of - 遍历值
for (const value of arr) {
console.log(value); // 'a', 'b', 'c'
}
// for...in - 遍历索引/属性名
for (const index in arr) {
console.log(index); // '0', '1', '2'
}
// 对象遍历
const obj = { name: 'John', age: 30 };
for (const key in obj) {
console.log(key, obj[key]);
}
// 迭代器
const str = 'hello';
for (const char of str) {
console.log(char); // 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'
}5.9 ES6中的类
// 类定义
class Person {
// 构造函数
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 实例方法
sayHello() {
return `Hello, I'm ${this.name}`;
}
// Getter
get info() {
return `${this.name} is ${this.age} years old`;
}
// Setter
set age(newAge) {
if (newAge > 0) {
this._age = newAge;
}
}
get age() {
return this._age;
}
// 静态方法
static createAdult(name) {
return new Person(name, 18);
}
}
// 继承
class Employee extends Person {
constructor(name, age, jobTitle) {
super(name, age); // 调用父类构造函数
this.jobTitle = jobTitle;
}
// 重写方法
sayHello() {
return `${super.sayHello()} and I'm a ${this.jobTitle}`;
}
// 新方法
work() {
return `${this.name} is working as a ${this.jobTitle}`;
}
}
// 使用
const john = new Person('John', 30);
const employee = new Employee('Jane', 25, 'Developer');
console.log(john.sayHello()); // "Hello, I'm John"
console.log(employee.work()); // "Jane is working as a Developer"5.10 其他ES6特性
// Symbol - 唯一标识符
const id = Symbol('description');
const user = {
name: 'John',
[id]: 12345
};
// 模块导入导出
// math.js
export const PI = 3.14159;
export function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
// main.js
import { PI, add } from './math.js';
// Promise - 异步处理
const fetchData = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Data loaded');
}, 1000);
});
};
// Map 和 Set
const map = new Map();
map.set('name', 'John');
map.set(1, 'number key');
const set = new Set([1, 2, 3, 3, 4]); // 自动去重6. 异步编程
6.1 Promise
// 创建Promise
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 异步操作
setTimeout(() => {
const success = true;
if (success) {
resolve('Operation successful');
} else {
reject('Operation failed');
}
}, 1000);
});
// 使用Promise
promise
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error(error))
.finally(() => console.log('Operation completed'));
// Promise链
function fetchUser(id) {
return fetch(`/api/users/${id}`)
.then(response => response.json());
}
function fetchUserPosts(userId) {
return fetch(`/api/users/${userId}/posts`)
.then(response => response.json());
}
// 链式调用
fetchUser(1)
.then(user => fetchUserPosts(user.id))
.then(posts => console.log(posts))
.catch(error => console.error(error));6.2 Async/Await
// async函数声明
async function fetchUserData(userId) {
try {
const user = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}`);
const userData = await user.json();
const posts = await fetch(`/api/users/${userId}/posts`);
const userPosts = await posts.json();
return { user: userData, posts: userPosts };
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching data:', error);
throw error;
}
}
// 箭头async函数
const fetchData = async () => {
const response = await fetch('/api/data');
return response.json();
};
// 并行执行
async function fetchMultipleData() {
const [users, posts, comments] = await Promise.all([
fetch('/api/users').then(r => r.json()),
fetch('/api/posts').then(r => r.json()),
fetch('/api/comments').then(r => r.json())
]);
return { users, posts, comments };
}
// 错误处理
async function robustFetch(url, retries = 3) {
for (let i = 0; i < retries; i++) {
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
return await response.json();
} catch (error) {
if (i === retries - 1) throw error;
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000 * Math.pow(2, i)));
}
}
}6.3 高级异步模式
// Promise.all - 所有Promise成功才成功
function fetchAllData() {
return Promise.all([
fetch('/api/users'),
fetch('/api/posts'),
fetch('/api/comments')
]);
}
// Promise.allSettled - 无论成功失败都返回结果
function fetchAllDataWithStatus() {
return Promise.allSettled([
fetch('/api/users'),
fetch('/api/posts'),
fetch('/api/comments')
]).then(results => {
results.forEach((result, index) => {
if (result.status === 'fulfilled') {
console.log(`Request ${index} succeeded:`, result.value);
} else {
console.log(`Request ${index} failed:`, result.reason);
}
});
});
}
// Promise.race - 返回最快完成的Promise
function fetchWithTimeout(url, timeout = 5000) {
return Promise.race([
fetch(url),
new Promise((_, reject) =>
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error('Timeout')), timeout)
)
]);
}
// 串行执行
async function processSequentially(items) {
const results = [];
for (const item of items) {
const result = await processItem(item);
results.push(result);
}
return results;
}7. 函数式编程
7.1 高阶函数
// map - 转换数组
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const doubled = numbers.map(n => n * 2); // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
const users = [
{ name: 'John', age: 30 },
{ name: 'Jane', age: 25 }
];
const names = users.map(user => user.name); // ['John', 'Jane']
// filter - 过滤数组
const evenNumbers = numbers.filter(n => n % 2 === 0); // [2, 4]
const adults = users.filter(user => user.age >= 18);
// reduce - 累积计算
const sum = numbers.reduce((acc, n) => acc + n, 0); // 15
const userNamesString = users.reduce((acc, user) =>
acc + user.name + ', ', '').slice(0, -2); // "John, Jane"
// 组合使用
const totalAgeOfAdults = users
.filter(user => user.age >= 18)
.reduce((total, user) => total + user.age, 0);7.2 函数组合
// 函数组合
const compose = (...fns) => (x) => fns.reduceRight((v, f) => f(v), x);
const pipe = (...fns) => (x) => fns.reduce((v, f) => f(v), x);
// 使用示例
const addOne = x => x + 1;
const multiplyByTwo = x => x * 2;
const toString = x => x.toString();
const addOneThenMultiplyByTwo = pipe(addOne, multiplyByTwo); // (x) => (x + 1) * 2
const result = addOneThenMultiplyByTwo(5); // 12
// 柯里化
const curry = (fn) => {
return function curried(...args) {
if (args.length >= fn.length) {
return fn.apply(this, args);
}
return (...nextArgs) => curried(...args, ...nextArgs);
};
};
const add = (a, b, c) => a + b + c;
const curriedAdd = curry(add);
console.log(curriedAdd(1)(2)(3)); // 6
console.log(curriedAdd(1, 2)(3)); // 67.3 实用函数式工具
// 记忆化
const memoize = (fn) => {
const cache = new Map();
return (...args) => {
const key = JSON.stringify(args);
if (cache.has(key)) {
return cache.get(key);
}
const result = fn(...args);
cache.set(key, result);
return result;
};
};
const fibonacci = memoize(n => {
if (n < 2) return n;
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
});
// 函数节流
const throttle = (fn, delay) => {
let lastCall = 0;
return (...args) => {
const now = Date.now();
if (now - lastCall >= delay) {
lastCall = now;
return fn(...args);
}
};
};
// 函数防抖
const debounce = (fn, delay) => {
let timeoutId;
return (...args) => {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => fn(...args), delay);
};
};
// 偏函数
const partial = (fn, ...presetArgs) => {
return (...laterArgs) => fn(...presetArgs, ...laterArgs);
};
const greet = (greeting, name) => `${greeting}, ${name}!`;
const sayHello = partial(greet, 'Hello');
console.log(sayHello('John')); // "Hello, John!"8. 现代JavaScript特性
8.1 ES2020+ 新特性
// 可选链操作符 (?.)
const user = {
name: 'John',
address: {
street: 'Main St'
}
};
const street = user?.address?.street; // 'Main St'
const zipCode = user?.address?.zipCode; // undefined
const phone = user?.contact?.phone; // undefined
// 空值合并操作符 (??)
const name = user.name ?? 'Anonymous'; // 'John'
const age = user.age ?? 0; // 0 (不会因为age=0而使用默认值)
// BigInt
const bigNumber = 123456789012345678901234567890n;
const anotherBigNumber = BigInt("123456789012345678901234567890");
// String.prototype.matchAll
const regex = /t(e)(st(\d?))/g;
const str = 'test1test2';
for (const match of str.matchAll(regex)) {
console.log(match);
}
// globalThis
const globalObj = globalThis; // 浏览器中是window,Node.js中是global8.2 ES2021+ 新特性
// String.prototype.replaceAll
const message = 'Hello world, hello universe';
const newMessage = message.replaceAll('hello', 'hi'); // "Hi world, hi universe"
// Promise.any
const promises = [
Promise.reject('Error 1'),
Promise.reject('Error 2'),
Promise.resolve('Success')
];
Promise.any(promises)
.then(result => console.log(result)) // "Success"
.catch(error => console.log(error)); // 所有Promise都失败时才执行
// 逻辑赋值操作符
let x = { name: 'John' };
// x.name &&= 'Jane'; // 相当于 x.name && (x.name = 'Jane')
// x.age ||= 25; // 相当于 x.age || (x.age = 25)
// x.city ??= 'NYC'; // 相当于 x.city ?? (x.city = 'NYC')
// 数组groupBy (ES2023)
const people = [
{ name: 'Alice', age: 25 },
{ name: 'Bob', age: 30 },
{ name: 'Charlie', age: 25 }
];
// const groupedByAge = Object.groupBy(people, person => person.age);
// 结果: { 25: [{...}, {...}], 30: [{...}] }8.3 数组新方法
// Array.prototype.flat / flatMap
const nestedArray = [1, [2, 3], [4, [5, 6]]];
const flatArray = nestedArray.flat(2); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
const sentences = ['Hello world', 'How are you', 'Goodbye'];
const words = sentences.flatMap(sentence => sentence.split(' '));
// ['Hello', 'world', 'How', 'are', 'you', 'Goodbye']
// Array.prototype.at
const arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
console.log(arr.at(0)); // 10
console.log(arr.at(-1)); // 50 (从末尾开始)
console.log(arr.at(-2)); // 40
// Array.prototype.findLast / findLastIndex
const numbers = [1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6];
const lastEven = numbers.findLast(n => n % 2 === 0); // 6
const lastEvenIndex = numbers.findLastIndex(n => n % 2 === 0); // 59. 错误处理与调试
9.1 错误处理模式
// 自定义错误类
class ValidationError extends Error {
constructor(message, field) {
super(message);
this.name = 'ValidationError';
this.field = field;
}
}
class NetworkError extends Error {
constructor(message, statusCode) {
super(message);
this.name = 'NetworkError';
this.statusCode = statusCode;
}
}
// 错误处理装饰器
const withErrorHandling = (fn) => {
return (...args) => {
try {
return fn(...args);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error in ${fn.name}:`, error.message);
// 可以在这里添加错误报告逻辑
throw error;
}
};
};
// Result模式 - 不使用异常
class Result {
constructor(success, value = null, error = null) {
this.success = success;
this.value = value;
this.error = error;
}
static success(value) {
return new Result(true, value);
}
static failure(error) {
return new Result(false, null, error);
}
map(fn) {
return this.success ? Result.success(fn(this.value)) : this;
}
flatMap(fn) {
return this.success ? fn(this.value) : this;
}
}
// 使用示例
function divide(a, b) {
if (b === 0) {
return Result.failure(new Error('Division by zero'));
}
return Result.success(a / b);
}
const result = divide(10, 2)
.map(x => x * 2)
.flatMap(x => divide(x, 5));9.2 调试技巧
// console方法
const user = { name: 'John', age: 30, address: { city: 'NYC' } };
console.log(user); // 基本日志
console.info(user); // 信息日志
console.warn(user); // 警告日志
console.error(user); // 错误日志
console.table([user, { name: 'Jane', age: 25 }]); // 表格显示
console.group('User Details');
console.log('Name:', user.name);
console.log('Age:', user.age);
console.groupEnd();
// 断言调试
const assert = (condition, message) => {
if (!condition) {
throw new Error(`Assertion failed: ${message}`);
}
};
// 性能测量
const measureTime = (fn, label) => {
console.time(label);
const result = fn();
console.timeEnd(label);
return result;
};
// 调试工具函数
const debug = (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development')
? (...args) => console.log('[DEBUG]', ...args)
: () => {};
const trace = (label) => {
console.trace(`Trace: ${label}`);
};10. 性能优化
10.1 内存管理
// 避免内存泄漏
class EventManager {
constructor() {
this.listeners = new Map();
}
addListener(event, callback) {
if (!this.listeners.has(event)) {
this.listeners.set(event, new Set());
}
this.listeners.get(event).add(callback);
}
removeListener(event, callback) {
if (this.listeners.has(event)) {
this.listeners.get(event).delete(callback);
}
}
emit(event, ...args) {
if (this.listeners.has(event)) {
this.listeners.get(event).forEach(callback => callback(...args));
}
}
// 清理所有监听器
cleanup() {
this.listeners.clear();
}
}
// WeakMap和WeakSet的使用
const weakMap = new WeakMap();
const weakSet = new WeakSet();
// 当对象被垃圾回收时,WeakMap中的对应条目也会被清理
const obj = { data: 'some data' };
weakMap.set(obj, 'metadata');
// 避免闭包内存泄漏
function createLeakFreeFunction() {
const largeData = new Array(1000000).fill('data');
return function useData(index) {
// 只访问需要的数据,不保持对largeData的引用
return largeData[index];
};
}10.2 执行优化
// 函数去抖和节流的应用场景
const searchInput = document.getElementById('search');
// 搜索去抖 - 避免频繁请求
const debouncedSearch = debounce((query) => {
fetch(`/api/search?q=${query}`)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(results => displayResults(results));
}, 300);
searchInput.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
debouncedSearch(e.target.value);
});
// 滚动节流 - 优化性能
const throttledScroll = throttle(() => {
updateScrollPosition();
}, 100);
window.addEventListener('scroll', throttledScroll);
// 批量DOM操作
const updateDOM = (() => {
const updates = [];
let rafId = null;
return (element, property, value) => {
updates.push({ element, property, value });
if (!rafId) {
rafId = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
updates.forEach(({ element, property, value }) => {
element[property] = value;
});
updates.length = 0;
rafId = null;
});
}
};
})();
// 虚拟滚动示例
class VirtualList {
constructor(container, itemHeight, renderItem) {
this.container = container;
this.itemHeight = itemHeight;
this.renderItem = renderItem;
this.visibleItems = [];
this.scrollTop = 0;
this.container.addEventListener('scroll', this.handleScroll.bind(this));
}
setItems(items) {
this.items = items;
this.updateVisibleItems();
}
handleScroll() {
this.scrollTop = this.container.scrollTop;
this.updateVisibleItems();
}
updateVisibleItems() {
const containerHeight = this.container.clientHeight;
const startIndex = Math.floor(this.scrollTop / this.itemHeight);
const endIndex = Math.min(
startIndex + Math.ceil(containerHeight / this.itemHeight) + 1,
this.items.length
);
// 只渲染可见的元素
this.container.innerHTML = '';
for (let i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) {
const item = this.renderItem(this.items[i], i);
item.style.position = 'absolute';
item.style.top = `${i * this.itemHeight}px`;
item.style.height = `${this.itemHeight}px`;
this.container.appendChild(item);
}
}
}10.3 代码分割与懒加载
// 动态导入
async function loadModule() {
try {
const module = await import('./heavy-module.js');
module.doSomething();
} catch (error) {
console.error('Module loading failed:', error);
}
}
// 条件加载
async function loadFeature() {
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
const { registerServiceWorker } = await import('./sw.js');
registerServiceWorker();
}
}
// React中的懒加载模式示例
class LazyComponent {
constructor() {
this.component = null;
this.loading = false;
}
async load() {
if (!this.component && !this.loading) {
this.loading = true;
try {
const module = await import('./Component.js');
this.component = module.default;
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
}
return this.component;
}
async render(container) {
const Component = await this.load();
if (Component) {
new Component(container);
}
}
}11. 模块化开发
11.1 ES6模块
// math.js - 导出
export const PI = 3.14159;
export function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
export function subtract(a, b) {
return a - b;
}
// 默认导出
export default function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
// main.js - 导入
import multiply, { add, subtract, PI } from './math.js';
import * as math from './math.js'; // 导入所有
// 动态导入
async function useMathModule() {
const math = await import('./math.js');
console.log(math.add(2, 3));
}11.2 模块设计模式
// 单例模块
const AppConfig = (() => {
let instance = null;
class Config {
constructor() {
this.settings = {};
}
set(key, value) {
this.settings[key] = value;
}
get(key) {
return this.settings[key];
}
getAll() {
return { ...this.settings };
}
}
return {
getInstance: () => {
if (!instance) {
instance = new Config();
}
return instance;
}
};
})();
// 观察者模式
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
this.events = new Map();
}
on(event, callback) {
if (!this.events.has(event)) {
this.events.set(event, new Set());
}
this.events.get(event).add(callback);
}
off(event, callback) {
if (this.events.has(event)) {
this.events.get(event).delete(callback);
}
}
emit(event, ...args) {
if (this.events.has(event)) {
this.events.get(event).forEach(callback => callback(...args));
}
}
}
// 状态管理器
class Store {
constructor(initialState = {}) {
this.state = { ...initialState };
this.listeners = new Set();
}
setState(updates) {
this.state = { ...this.state, ...updates };
this.notify();
}
getState() {
return { ...this.state };
}
subscribe(listener) {
this.listeners.add(listener);
return () => this.listeners.delete(listener);
}
notify() {
this.listeners.forEach(listener => listener(this.state));
}
}12. 测试与质量保证
12.1 单元测试
// 简单的测试框架
class TestRunner {
constructor() {
this.tests = [];
this.results = {
passed: 0,
failed: 0,
errors: []
};
}
test(name, fn) {
this.tests.push({ name, fn });
}
async run() {
console.log('Running tests...');
for (const test of this.tests) {
try {
await test.fn();
console.log(`✓ ${test.name}`);
this.results.passed++;
} catch (error) {
console.log(`✗ ${test.name}`);
console.log(` Error: ${error.message}`);
this.results.failed++;
this.results.errors.push({ test: test.name, error });
}
}
console.log(`
Results: ${this.results.passed} passed, ${this.results.failed} failed`);
return this.results;
}
}
// 断言函数
function assert(condition, message = 'Assertion failed') {
if (!condition) {
throw new Error(message);
}
}
function assertEqual(actual, expected, message) {
assert(actual === expected,
message || `Expected ${expected}, but got ${actual}`);
}
function assertThrows(fn, message) {
let threw = false;
try {
fn();
} catch (error) {
threw = true;
}
assert(threw, message || 'Expected function to throw');
}
// 测试示例
const runner = new TestRunner();
runner.test('Array.prototype.map works correctly', () => {
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const result = arr.map(x => x * 2);
assertEqual(result.length, 3);
assertEqual(result[0], 2);
assertEqual(result[1], 4);
assertEqual(result[2], 6);
});
runner.test('Error handling in division', () => {
function divide(a, b) {
if (b === 0) {
throw new Error('Division by zero');
}
return a / b;
}
assertEqual(divide(10, 2), 5);
assertThrows(() => divide(10, 0));
});12.2 性能测试
// 性能测试工具
class PerformanceTester {
static async measureTime(fn, iterations = 1000) {
const start = performance.now();
for (let i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
await fn();
}
const end = performance.now();
return (end - start) / iterations;
}
static compare(fns, iterations = 1000) {
return Promise.all(
fns.map(async (fn, index) => ({
name: fn.name || `Function ${index}`,
time: await this.measureTime(fn, iterations)
}))
).then(results =>
results.sort((a, b) => a.time - b.time)
);
}
}
// 内存使用测试
function measureMemoryUsage(fn) {
if (typeof performance !== 'undefined' && performance.memory) {
const before = performance.memory.usedJSHeapSize;
fn();
const after = performance.memory.usedJSHeapSize;
return after - before;
}
return null;
}总结
本文档全面覆盖了现代JavaScript开发的核心概念和最佳实践,从基础语法到高级特性,从同步编程到异步处理,从性能优化到测试方法。通过系统学习这些内容,你将能够:
- 掌握现代JavaScript语法和特性
- 理解异步编程和事件循环机制
- 运用函数式编程思想
- 编写高性能、可维护的代码
- 进行有效的错误处理和调试
- 实施模块化开发架构
JavaScript生态系统在不断演进,保持学习热情和关注最新标准是关键。建议定期查看TC39提案和MDN文档,及时掌握新特性。
参考资源
官方文档
学习资源
工具与框架
性能优化
最后更新:2024年版本:v2.0文档维护者:前端开发团队
继续探索,持续进步!🚀
